Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Outlier detection with DBSCAN and spline regression 002
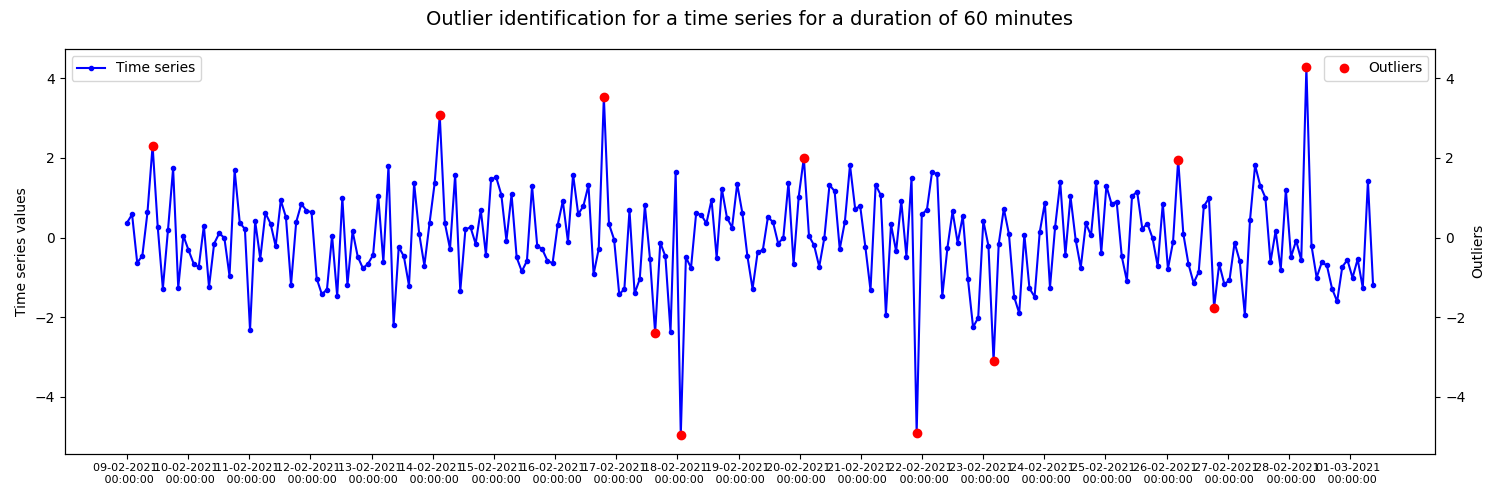
Example of outlier detection in a randomly generated time series data using DBSCAN and spline regression. The resulting figure shows outliers generated with a time window of 60min marked on the original time series.
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from indsl.statistics.outliers import detect_outliers
# Generate time series with outliers
rng1 = np.random.default_rng(0)
mu = 0
sigma = 1
outliers_positive = rng1.uniform(low=3 * sigma, high=5 * sigma, size=2)
outliers_negative = rng1.uniform(low=-5 * sigma, high=-3 * sigma, size=2)
values = np.concatenate((outliers_positive, outliers_negative, rng1.normal(mu, sigma, 240)), axis=0)
rng1.shuffle(values)
data = pd.Series(values, index=pd.date_range("2021-02-09 00:00:00", "2021-03-01 09:00:00", periods=244))
# Plot outliers against actual data
fig, ax1 = plt.subplots(figsize=(15, 5))
# Plot actual time series data
ax1.plot(data.index, data, label="Time series", marker=".", color="blue")
ts_values = np.arange(data.index[0], data.index[-1], timedelta(days=1)).astype(datetime)
ax1.set_xticks(ts_values)
ax1.set_xticklabels([ts.strftime("%d-%m-%Y \n %H:%M:%S") for ts in ts_values], fontsize=8)
# Plot outliers indicator time series
ax2 = ax1.twinx()
ax2.plot(
data[np.where(detect_outliers(data) == 1)[0]].index,
data[np.where(detect_outliers(data) == 1)[0]].values,
"o",
color="red",
label="Outliers",
)
# Place legend
ax1.legend(loc="upper left")
ax2.legend(loc="upper right")
plt.xlabel("Timestamp")
ax1.set_ylabel("Time series values")
ax2.set_ylabel("Outliers")
fig.suptitle("Outlier identification for a time series for a duration of 60 minutes", fontsize=14)
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.274 seconds)