Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Data smoothing with the Savitzky-Golay filter
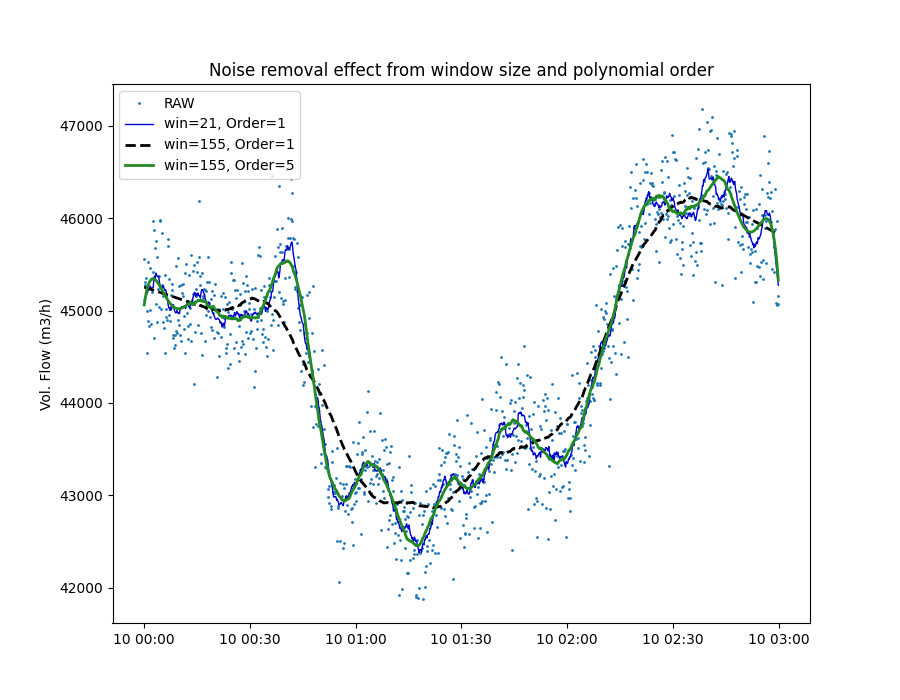
Example of noise removal from time series data using the Savitzky-Golay smoother. We use data from volumetric flow rate (m3/h) sensor with non-uniform sampling frequency measuring flow into a compressor.
In the figure below it can be observed how a small window size (win=21) and linear fit (order=1) exposes the trend and some of the noise (data fluctuations). Increasing the window size while keeping a linear fit results in a stronger smoothing of the data. However, increasing the order of the fit to 5 (non-linear fit) produced a nice and smooth trend while allowing the larger fluctuation through.
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
from indsl.smooth import sg
base_path = "" if __name__ == "__main__" else os.path.dirname(__file__)
data = pd.read_csv(os.path.join(base_path, "../../datasets/data/vol_flow_rate_m3h.csv"), index_col=0)
data = data.squeeze()
data.index = pd.to_datetime(data.index)
# TODO: Create load_flowrate_data method from above
# Apply the smoother with different settings and plot the results
plt.figure(1, figsize=[9, 7])
plt.plot(data, ".", markersize=2, label="RAW")
# Short window, order =1 (linear)
plt.plot(sg(data, window_length=21, polyorder=1), color="mediumblue", linewidth=1, label="win=21, Order=1")
# Long window, order =1 (linear)
plt.plot(sg(data, window_length=155, polyorder=1), color="k", linewidth=2, ls="--", label="win=155, Order=1")
# Long window, order =5 (non-linear)
plt.plot(sg(data, window_length=155, polyorder=5), color="forestgreen", linewidth=2, ls="-", label="win=155, Order=5")
plt.ylabel("Vol. Flow (m3/h)")
plt.title("Noise removal effect from window size and polynomial order")
_ = plt.legend(loc=2)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.154 seconds)